Company
 About Us About Us
 Management Management
 Advisors Advisors
 Contact Us Contact Us
Technology
 APOE and Human APOE and Human
 Disease Disease
 APOE and APOE and
 Inflammation Inflammation
 Cognosci APOE Cognosci APOE
 Compounds Compounds
 Publications Publications
Pipeline
 Multiple Sclerosis Multiple Sclerosis
 Traumatic Brain Traumatic Brain
 Injury Injury
 Subarachnoid Subarachnoid
 Hemorrhage Hemorrhage
 Rheumatoid Arthritis Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Ischemic Stroke Ischemic Stroke
 Sepsis Sepsis
 Alzheimer’s Disease Alzheimer’s Disease
 Parkinson’s Disease Parkinson’s Disease
Partnering
 Multiple Sclerosis Multiple Sclerosis
 Alzheimer’s Disease Alzheimer’s Disease
 Subarachnoid Subarachnoid
 Hemorrhage Hemorrhage
News
 Latest News Latest News
|

|
APOE and Human Disease
 Humans are the only species to express multiple isoforms of apolipoprotein-E (the APOE gene encodes the apoE protein). One of these isoforms, apoE4, is more frequently found in patients with Alzheimer's disease (AD), than in their non-diseased counterparts, suggesting that apoE may play a role in disease. This discovery led to additional investigations of other diseases where the presence of apoE4 was associated with a more severe form of the disease and/or with an earlier onset of the disease.
Humans are the only species to express multiple isoforms of apolipoprotein-E (the APOE gene encodes the apoE protein). One of these isoforms, apoE4, is more frequently found in patients with Alzheimer's disease (AD), than in their non-diseased counterparts, suggesting that apoE may play a role in disease. This discovery led to additional investigations of other diseases where the presence of apoE4 was associated with a more severe form of the disease and/or with an earlier onset of the disease.
These associations between the presence of apoE4 and a worse disease have been reported for Alzheimer's Disease (AD), Multiple Sclerosis (MS), Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI), Subarchnoid Hemorrhage (SAH), Intracranial Hemorrhage (ICH), Stroke, Dementia Puglistica, Parkinson's Disease (PD) and others. Unlike some genes and their protein products that cause a disease, APOE4 is not a disease-causing gene. The APOE4 gene and its apoE4-protein product are significant risk factors that predispose an enhanced susceptibility to each of these disabling diseases.
How do apoE-protein isoforms influence the disease state? The best-known role of apoE is in the control of cholesterol levels. APOE2 carriers (about 7% of the general population) have very high levels of cholesterol in their blood compared to normal cholesterol levels in APOE3 carriers (about 78% of the population) and in APOE4 carriers (about 14% of the population). Interestingly, APOE2 carriers appear to be protected from Alzheimer's while APOE4 carriers are especially susceptible to the disease.
Although the largest group of APOE3 carriers do develop Alzheimer's, their cholesterol levels are similar to those in APOE4 patients and thus, cholesterol is probably not a key factor in AD or in these other diseases. On the plus side, when cells are damaged by disease they require large amounts of cholesterol to rebuild. Damaged cells typically express high levels of apoE-receptors that then bind the apoE contained in lipoprotein particles and deliver large amounts of cholesterol for the cells rebuilding needs.
In addition to the presence of apoE4, however, each of these diseases is significantly associated with inflammation of the brain. Our studies have shown that the inflammation in each of these diseases is worse when apoE4 is present. This finding opens a therapeutic way forward to change inflammation leading to a change in the course of the disease.
Apolipoprotein-E and Inflammation
Patients who are carriers of the APOE4 gene are more susceptible to certain diseases than their APOE3 counterparts. The precise mechanism underlying this APOE-gene-specific difference, however, is not well understood. We have shown that APOE4 carriers are more inflamed than their APOE3 counterparts.

|
Hypothesis:
APOE3 gene products inhibit inflammation more than APOE4 gene products.
|

|
Proposal:
Find and isolate the region of apoE3 protein that possesses this anti-inflammatory activity.
|

|
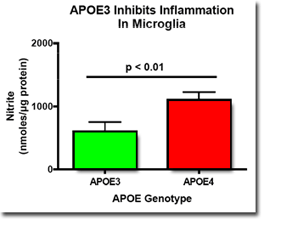
APOE3 inhibits inflammation more than APOE4 in primary microglia cultures derived from mouse brain. Cultured microglia from APOE3/3 transgenic replacement mice and from APOE4/4 transgenic replacement mice were treated with gamma interferon plus lipopolysaccharide for 24 hours and nitrite, the stable oxidation product of nitric oxide, was measured in conditioned media using the Greiss method.
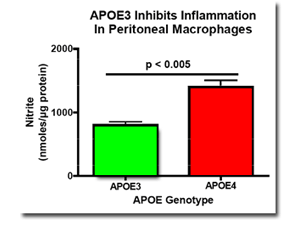
APOE3 inhibits inflammation more than APOE4 in peritoneal macrophages derived from APOE3/3 transgenic replacement mice and from APOE4/4 transgenic replacement mice. Cultured macrophages were treated with gamma interferon plus lipopolysaccharide for 24 hours and nitrite, the stable oxidation product of nitric oxide, was measured in conditioned media using the Greiss method.
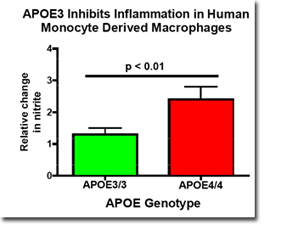
APOE3 inhibits inflammation more than APOE4 in human monocytes derived macrophages derived from human APOE3/3 and from human APOE4/4 volunteers. Cultured macrophages were treated with double-stranded RNA (poly-inosine: poly-cytidine) for 72 hours and nitrite, the stable oxidation product of nitric oxide, was measured with a Siever's nitric oxide analyzer.

Cognosci's apoE Compounds Inhibit Inflammation
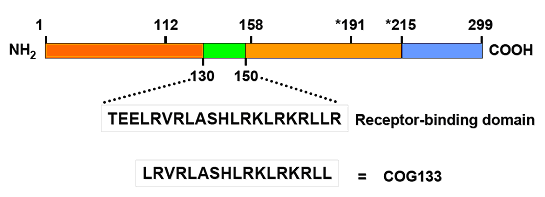
The mature apoE-protein is 299 amino acids in length. Polymorphisms that distinguish the different apoE-isoforms encode cysteine residues at positions 112 and 158 in the apoE2-isoform, a cysteine and an arginine in the apoE3-isoform and arginine residues at both positions in the apoE4-isoform. We initially focused on the receptor-binding domain to create peptides that might mimic the effects of the mature apoE3-protein. Starting with COG133, which spans residues from 133 to 149, we created a series of apoE-derived peptides and tested each one for anti-inflammatory activity.
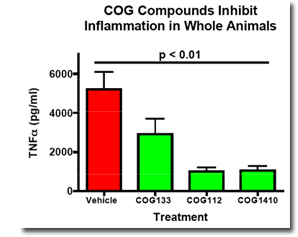
Mice were treated with lipopolysaccharide followed by vehicle, COG133, COG112 or COG1410. After 60 minutes, blood was drawn and the amount of Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF) alpha in the plasma was measured by Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA).

COG Compounds Are Neuroprotective
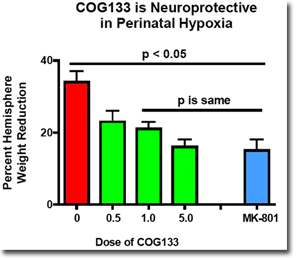
Another important aspect of a useful neuro-restorative compound is its ability to protect neurons from the types of challenges that are associated with neuronal dysfunction and death. We have used whole animals to demonstrate that COG133 can effectively inhibit loss of brain mass following a perinatal hypoxia challenge. Together with previous studies showing that COG133 can inhibit neuronal death after challenge with N-methyl-D-asparate (an excitatory neurotoxin), these data show that COG133 is a useful and effective neuroprotective compound.

Publications
Publications Including Cognosci's Efforts:

|

|
An apolipoprotein E-based therapeutic improves outcome and reduces Alzheimer's disease pathology following closed head injury: Evidence of pharmacogenomic interaction
|

|
Wang H, Durham L, Dawson H, Song P, Warner DS, Sullivan PM, Vitek MP, Laskowitz DT
|

|
Neuroscience. 2007 Feb 23; 144(4):1324-33. Epub 2006 Dec 20
|

|

|
Dissociation between vasospasm and functional improvement in a murine model of subarachnoid hemorrhage
|

|
Mesis RG, Wang H, Lombard FW, Yates R, Vitek MP, Borel CO, Warner DS, Laskowitz DT
|

|
Neurosurg Focus. 2006 Sep 15; 21(3):E4
|

|

|
Apolipoprotein E-derived peptides reduce CNS inflammation: implications for therapy of neurological disease
|

|
Laskowitz DT, Fillit H, Yeung N, Toku K, Vitek MP
|

|
Acta Neurol Scand Suppl. 2006; 185:15-20. Review
|

|

|
Apolipoprotein E-derived peptides ameliorate clinical disability and inflammatory infiltrates into the spinal cord in a murine model of multiple sclerosis
|

|
Li FQ, Sempowski GD, McKenna SE, Laskowitz DT, Colton CA, Vitek MP
|

|
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2006 Sep;318(3): 956-65. Epub 2006 Jun 1
|

|

|
A novel apoE-derived therapeutic reduces vasospasm and improves outcome in a murine model of subarachnoid hemorrhage
|

|
Gao J, Wang H, Sheng H, Lynch JR, Warner DS, Durham L, Vitek MP, Laskowitz DT
|

|
Neurocrit Care. 2006; 4(1):25-31
|

|

|
Intrathecal administration of a novel apoE-derived therapeutic peptide improves outcome following perinatal hypoxic-ischemic injury
|

|
McAdoo JD, Warner DS, Goldberg RN, Vitek MP, Pearlstein R, Laskowitz DT
|

|
Neurosci Lett. 2005 Jun 24; 381(3):305-8
|

|

|
A novel therapeutic derived from apolipoprotein E reduces brain inflammation and improves outcome after closed head injury
|

|
Lynch JR, Wang H, Mace B, Leinenweber S, Warner DS, Bennett ER, Vitek MP, McKenna S, Laskowitz DT
|

|
Exp Neurol. 2005 Mar; 192(1):109-16
|

|

|
Use of a multiple-enzyme/multiple-reagent assay system to quantify activity levels in samples containing mixtures of matrix metalloproteinases
|

|
Rasmussen FH, Yeung N, Kiefer L, Murphy G, Lopez-Otin C, Vitek MP, Moss ML
|

|
Biochemistry. 2004 Mar 23; 43(11):2987-95
|

|

|
APOE genotype and an ApoE-mimetic peptide modify the systemic and central nervous system inflammatory response
|

|
Lynch JR, Tang W, Wang H, Vitek MP, Bennett ER, Sullivan PM, Warner DS, Laskowitz DT
|

|
J Biol Chem. 2003 Dec 5; 278(49):48529-33. Epub 2003 Sep 24
|
Publications Supporting Cognosci's Therapeutic Compounds:

|

|
Expression profiles for macrophage alternative activation genes in AD and in mouse models of AD
|

|
Colton CA, Mott RT, Sharpe H, Xu Q, Van Nostrand WE, Vitek MP
|

|
J Neuroinflammation. 2006 Sep 27; 3:27
|

|

|
Sex steroids, APOE genotype and the innate immune system
|

|
Colton CA, Brown CM, Vitek MP
|

|
Neurobiol Aging. 2005 Mar; 26(3):363-72. Review.
|

|

|
Disrupted spermine homeostasis: a novel mechanism in polyglutamine-mediated aggregation and cell death
|

|
Colton CA, Xu Q, Burke JR, Bae SY, Wakefield JK, Nair A, Strittmatter WJ, Vitek MP
|

|
J Neurosci. 2004 Aug 11; 24(32):7118-27
|

|

|
APOE genotype-specific differences in human and mouse macrophage nitric oxide production
|

|
Colton CA, Needham LK, Brown C, Cook D, Rasheed K, Burke JR, Strittmatter WJ, Schmechel DE, Vitek MP
|

|
J Neuroimmunol. 2004 Feb; 147(1-2):62-7
|

|

|
APOE and the regulation of microglial nitric oxide production: a link between genetic risk and oxidative stress
|

|
Colton CA, Brown CM, Cook D, Needham LK, Xu Q, Czapiga M, Saunders AM, Schmechel DE, Rasheed K, Vitek MP
|

|
Neurobiol Aging. 2002 Sep-Oct; 23(5):777-85
|

|

|
Apolipoprotein E isoform mediated regulation of nitric oxide release
|

|
Brown CM, Wright E, Colton CA, Sullivan PM, Laskowitz DT, Vitek MP
|

|
Free Radic Biol Med. 2002 Jun 1; 32(11):1071-5
|

|

|
Apolipoprotein E acts to increase nitric oxide production in macrophages by stimulating arginine transport
|

|
Colton CA, Czapiga M, Snell-Callanan J, Chernyshev ON, Vitek MP
|

|
Biochim Biophys Acta. 2001 Feb 14; 1535(2):134-44
|

|

|
Akt activation protects hippocampal neurons from apoptosis by inhibiting transcriptional activity of p53
|

|
Yamaguchi A, Tamatani M, Matsuzaki H, Namikawa K, Kiyama H, Vitek MP, Mitsuda N, Tohyama M
|

|
J Biol Chem. 2001 Feb 16; 276(7):5256-64. Epub 2000 Oct 27
|

|

|
Apolipoprotein E mimetic Peptide dramatically lowers plasma cholesterol and restores endothelial function in watanabe heritable hyperlipidemic rabbits
|

|
Gupta H, White CR, Handattu S, Garber DW, Datta G, Chaddha M, Dai L, Gianturco SH, Bradley WA, Anantharamaiah GM
|

|
Circulation. 2005 Jun 14; 111(23):3112-8. Epub 2005 Jun 6
|

|

|
An apolipoprotein E-derived peptide mediates uptake of sterically stabilized liposomes into brain capillary endothelial cells
|

|
Sauer I, Dunay IR, Weisgraber K, Bienert M, Dathe M.
|

|
Biochemistry. 2005 Feb 15; 44(6):2021-9
|

|

|
Increased susceptibility to experimental autoimmune neuritis after upregulation of the autoreactive T cell response to peripheral myelin antigen in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice
|

|
Yu S, Duan RS, Chen Z, Quezada HC, Bao L, Nennesmo I, Zhu SW, Winblad B, Ljunggren HG, Zhu J.
|

|
J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2004 Feb; 63(2):120-8
|

|

|
Protective effect of apolipoprotein E-mimetic peptides on N-methyl-D-aspartate excitotoxicity in primary rat neuronal-glial cell cultures
|

|
Aono M, Bennett ER, Kim KS, Lynch JR, Myers J, Pearlstein RD, Warner DS, Laskowitz DT
|

|
Neuroscience. 2003; 116(2):437-45
|

|

|
Sustained-delivery of an apolipoprotein E-peptidomimetic using multivesicular liposomes lowers serum cholesterol levels
|

|
Ramprasad MP, Anantharamaiah GM, Garber DW, Katre NV
|

|
J Control Release. 2002 Feb 19; 79(1-3):207-18
|

|

|
Apolipoprotein E decreases tau kinases and phospho-tau levels in primary neurons
|

|
Hoe HS, Freeman J, Rebeck GW
|

|
Mol Neurodegener. 2006 Dec 13; 1:18
|

|

|
Two apolipoprotein E mimetic peptides, ApoE(130-149) and ApoE(141-155)2, bind to LRP1
|

|
Croy JE, Brandon T, Komives EA
|

|
Biochemistry. 2004 Jun 15; 43(23):7328-35
|

|

|
ApoE isoforms affect neuronal N-methyl-D-aspartate calcium responses and toxicity via receptor-mediated processes
|

|
Qiu Z, Crutcher KA, Hyman BT, Rebeck GW
|

|
Neuroscience. 2003; 122(2):291-303
|

|

|
Apolipoprotein E and Reelin ligands modulate tau phosphorylation through an apolipoprotein E receptor/disabled-1/glycogen synthase kinase-3beta cascade
|

|
Ohkubo N, Lee YD, Morishima A, Terashima T, Kikkawa S, Tohyama M, Sakanaka M, Tanaka J, Maeda N, Vitek MP, Mitsuda N.
|

|
FASEB J. 2003 Feb;17(2): 295-7. Epub 2002 Dec 18
|

|

|
Apolipoprotein E and mimetic peptide initiate a calcium-dependent signaling response in macrophages
|

|
Misra UK, Adlakha CL, Gawdi G, McMillian MK, Pizzo SV, Laskowitz DT
|

|
J Leukoc Biol. 2001 Oct; 70(4):677-83
|

|

|
Downregulation of microglial activation by apolipoprotein E and apoE-mimetic peptides
|

|
Laskowitz DT, Thekdi AD, Thekdi SD, Han SK, Myers JK, Pizzo SV, Bennett ER
|

|
Exp Neurol. 2001 Jan; 167(1):74-85
|

|

|
Apolipoprotein E4 stimulates cAMP response element-binding protein transcriptional activity through the extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway
|

|
Ohkubo N, Mitsuda N, Tamatani M, Yamaguchi A, Lee YD, Ogihara T, Vitek MP, Tohyama M
|

|
J Biol Chem. 2001 Feb 2; 276(5):3046-53. Epub 2000 Oct 20
|

|

|
Peptide model of a highly conserved, N-terminal domain of apolipoprotein E is able to modulate lipoprotein binding to a member of the class A scavenger receptor family
|

|
Dominguez SR, Miller-Auer H, Reardon CA, Meredith SC
|

|
J Lipid Res. 1999 Apr; 40(4):753-63
|

|

|
Identification of a neuronal endocytic pathway activated by an apolipoprotein E (apoE) receptor binding peptide
|

|
Wang X, Ciraolo G, Morris R, Gruenstein E
|

|
Brain Res. 1997 Dec 5; 778(1):6-15
|

|

|
Regulation of scavenger receptor, class B, type I, a high density lipoprotein receptor, in liver and steroidogenic tissues of the rat
|

|
Landschulz KT, Pathak RK, Rigotti A, Krieger M, Hobbs HH
|

|
J Clin Invest. 1996 Aug 15; 98(4):984-95
|

|

|
Structural features of synthetic peptides of apolipoprotein E that bind the LDL receptor
|

|
Dyer CA, Cistola DP, Parry GC, Curtiss LK
|

|
J Lipid Res. 1995 Jan; 36(1):80-8
|
|

|
Latest News
Cognosci Receives Funding for Advanced Testing of Lead Drug Candidate for the Treatment of Multiple Sclerosis
more...
For more information, contact:
Cognosci Inc.
79 T. W. Alexander Drive
4401 Research Commons
Research Triangle Park
NC 27709
(919) 765-0028
|